The Impact Of Tariffs On China's Export-Led Growth Model
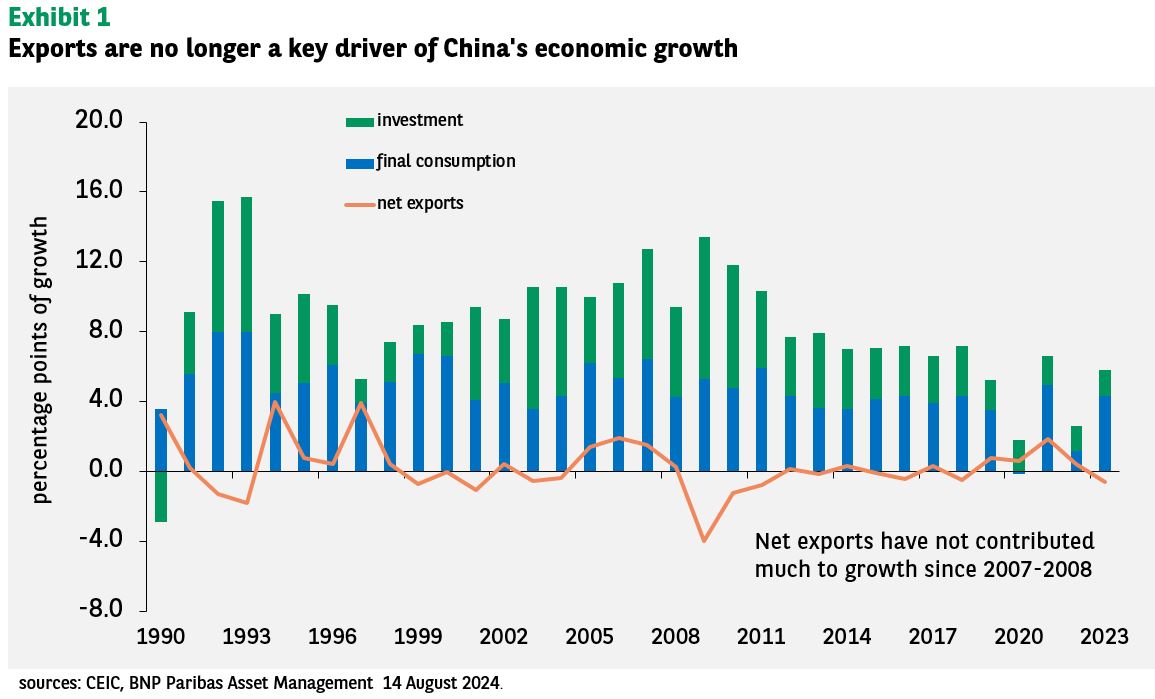
Table of Contents
China's remarkable economic growth over the past few decades has been significantly fueled by its export-led growth model. This strategy, focusing on manufacturing goods for global markets, propelled China to become the world's second-largest economy. However, the imposition of tariffs, particularly those stemming from the recent US-China trade war, has dramatically altered this trajectory. This article will explore the profound impact of tariffs on China's export-led growth model, examining the consequences for its economy and global trade relations.
Disruption of Global Supply Chains and Trade Flows
Keywords: supply chain disruption, global trade flows, import tariffs, export restrictions, trade diversion, China's manufacturing, global value chains.
Tariffs imposed on Chinese goods significantly increased their cost in international markets, reducing their competitiveness against products from other nations. This had a ripple effect throughout the global economy.
-
Increased Costs and Reduced Competitiveness: The added tariff costs were often passed on to consumers, making Chinese products less attractive compared to alternatives. This directly impacted the volume of Chinese exports.
-
Manufacturing Relocation: To avoid tariff penalties, many businesses chose to relocate their manufacturing operations outside of China, particularly to countries like Vietnam and Mexico. This disrupted long-established supply chains and created uncertainty for companies reliant on Chinese manufacturing.
-
Trade Diversion: Importers sought alternative sources for goods, leading to trade diversion. China experienced a decline in its market share as businesses opted for suppliers in countries not subject to the same tariffs. This significantly impacted the volume of Chinese exports across numerous sectors.
-
Global Value Chain Complexity: The intricate nature of global value chains amplified the challenges. Companies faced difficulties in quickly adapting their supply chains, leading to production delays, increased costs, and reduced efficiency. The uncertainty surrounding future tariff policies added to this complexity.
Impact on Specific Chinese Industries
Keywords: Chinese manufacturing, technology sector, agricultural exports, textile industry, tariff impact by sector, export diversification.
The impact of tariffs wasn't uniform across all Chinese industries. Some sectors were hit harder than others, highlighting the vulnerability of an export-dependent model.
-
Technology Sector: The technology sector faced particularly significant challenges. Restrictions on the export of high-tech products, coupled with tariffs, hampered growth and innovation. This sector is crucial for China's long-term economic aspirations.
-
Agricultural Exports: Retaliatory tariffs imposed by China on US agricultural products had a negative impact on US farmers and also affected the profitability of Chinese agricultural exports. The trade war highlighted the interconnectedness of global agricultural markets.
-
Textile Industry: Labor-intensive industries like textiles, already facing competition from lower-cost producers, saw further decline in export demand as tariffs increased prices and reduced competitiveness. This led to job losses and economic hardship in affected regions.
-
Varying Impacts: The impact of tariffs varied significantly across sectors. While some experienced major setbacks, others demonstrated more resilience, showcasing the need for diverse economic strategies.
Government Response and Economic Adjustment
Keywords: economic stimulus, domestic consumption, industrial policy, economic diversification, China's economic reforms.
Faced with the challenges posed by tariffs, the Chinese government implemented several strategies to mitigate the negative impact and adjust its economic approach.
-
Economic Stimulus Packages: The government rolled out economic stimulus packages aimed at boosting growth and supporting affected industries. These measures included infrastructure spending and tax cuts.
-
Focus on Domestic Consumption: There's been a concerted effort to stimulate domestic consumption to reduce reliance on exports for economic growth. This involves policies to increase disposable income and encourage domestic spending.
-
Industrial Policy and Technological Innovation: The government implemented industrial policies focused on promoting technological innovation and upgrading existing industries. This aims to improve competitiveness and reduce dependence on low-value-added manufacturing.
-
Export Diversification: Efforts are underway to diversify export markets and reduce over-reliance on specific trading partners. This is a crucial long-term strategy to mitigate future risks associated with trade disputes.
Long-Term Implications for China's Economic Growth
Keywords: sustainable growth, economic transformation, structural reforms, future of China's economy, global economic outlook.
The tariffs and resulting economic adjustments have significant long-term implications for China's economic trajectory. The export-led model, while successful for decades, may require a fundamental shift.
-
Shifting Growth Model: Sustainable economic growth will necessitate a move away from over-reliance on exports toward a more balanced model that prioritizes domestic demand and technological innovation.
-
Domestic Demand as a Driver: Increased domestic consumption is essential for sustaining economic growth. This requires further reforms to enhance income distribution and consumer confidence.
-
Structural Reforms: Deep structural reforms are critical to address economic imbalances, improve efficiency, and enhance the overall competitiveness of the Chinese economy.
-
Reshaping the Global Economic Landscape: The ongoing impact of tariffs and the resulting adjustments by China are likely to reshape the global economic landscape in the coming years, leading to a more multipolar trading system.
Conclusion
Tariffs have undeniably impacted China's export-led growth model, disrupting supply chains, affecting various industries, and prompting the government to implement significant economic adjustments. The long-term implications are substantial, necessitating a shift toward a more balanced and domestically driven economic strategy. Understanding the impact of tariffs on China's export-led growth model is crucial for navigating the evolving global economic landscape. Further research and analysis are needed to fully comprehend the long-term consequences and adapt strategies accordingly. Stay informed on the latest developments in China's export-led growth and the continuing impacts of global trade policies.

Featured Posts
-
 Sweden And Finland A Unified Defense Strategy For The Nordic Region
Apr 22, 2025
Sweden And Finland A Unified Defense Strategy For The Nordic Region
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Tik Tok Tariffs And Just Contact Us How Businesses Evade Trump Era Trade Restrictions
Apr 22, 2025
Tik Tok Tariffs And Just Contact Us How Businesses Evade Trump Era Trade Restrictions
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Trumps Trade Policies And The Future Of Us Financial Primacy
Apr 22, 2025
Trumps Trade Policies And The Future Of Us Financial Primacy
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Lab Owners Guilty Plea Faking Covid 19 Test Results During Pandemic
Apr 22, 2025
Lab Owners Guilty Plea Faking Covid 19 Test Results During Pandemic
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Just Contact Us On Tik Tok A Look At Post Trump Tariff Strategies
Apr 22, 2025
Just Contact Us On Tik Tok A Look At Post Trump Tariff Strategies
Apr 22, 2025
