Understanding Papal Conclaves: History, Secrecy, And The Election Of The Pope
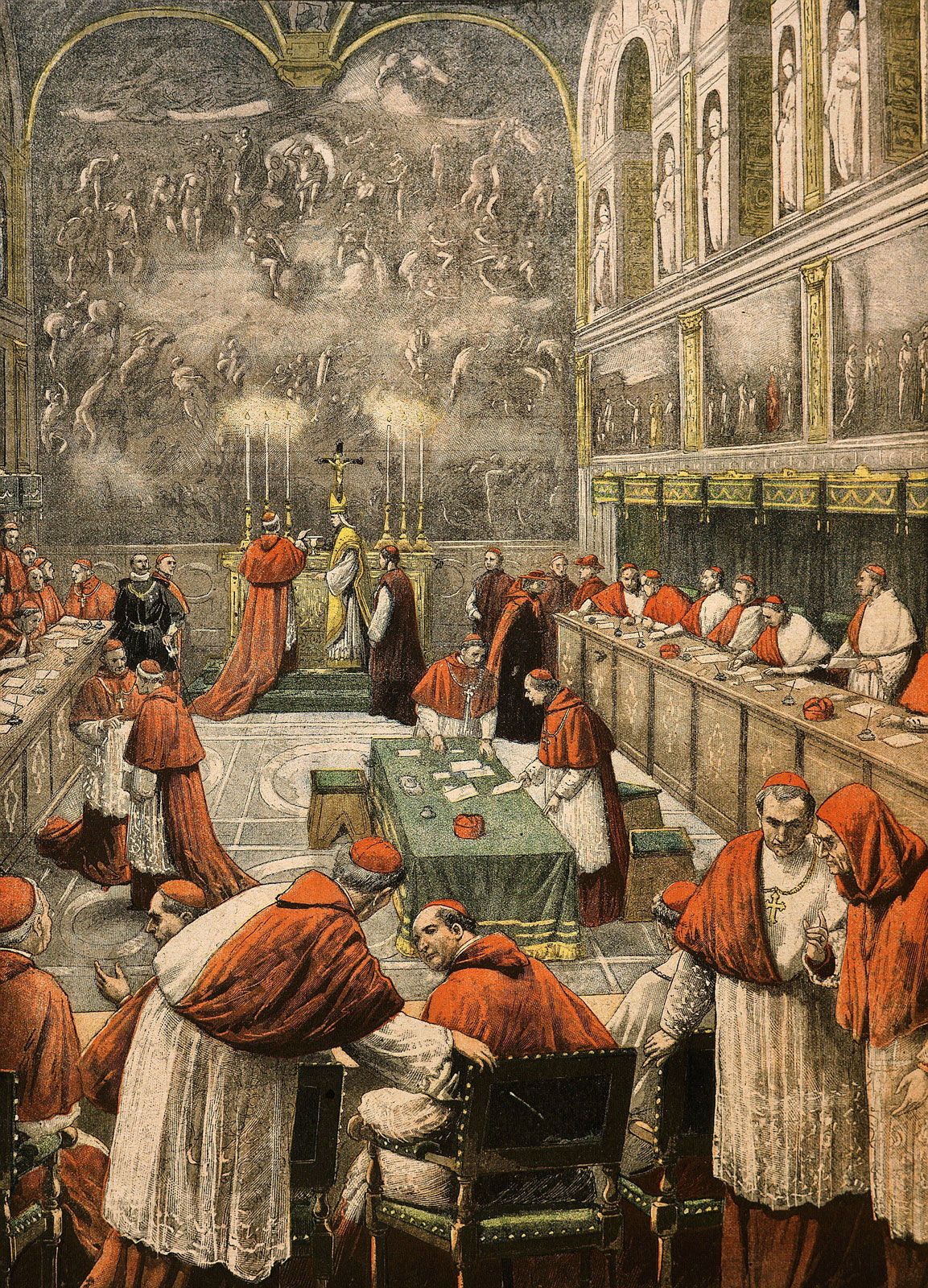
Table of Contents
A Brief History of Papal Conclaves
Early Papal Elections: Chaos and Controversy
Before the formalization of the Conclave, the election of Popes was often a chaotic and even violent affair. The process lacked clear rules, leading to significant problems:
- Simony: The buying and selling of ecclesiastical offices, including the Papacy, was rampant. Wealthy families and individuals frequently bribed their way to influence the election.
- Political Interference: Emperors and powerful secular rulers often exerted considerable influence, imposing their preferred candidates upon the Church. The election became a political battleground rather than a spiritual one.
- Violent Conflicts: Disputes over the election frequently erupted into open violence, with rival factions fighting for control.
Examples of this tumultuous period include the papal elections of the 9th and 10th centuries, which were often marked by long periods of vacancy and contested claims to the papacy, fueled by competing factions within the Roman nobility and interventions by the Holy Roman Emperors. The influence of powerful families, like the Counts of Tusculum, further destabilized the process.
The Evolution of Conclave Rules
Over centuries, the procedures surrounding Papal Conclaves gradually evolved, becoming more formalized and structured. Key papal decrees and council decisions helped shape the modern Conclave:
- The Second Lateran Council (1139): This council established important regulations, aiming to curb corruption and political interference.
- Papal Bulls and Decrees: Various Popes issued decrees throughout the centuries, refining the rules and procedures of the Conclave.
- Gregory X's Reforms (1274): Pope Gregory X, responding to a long and contentious Papal election, introduced significant reforms that form the basis of many of the modern Conclave's practices. This included the confinement of the cardinals to a single location.
These reforms were crucial in establishing a more structured and less susceptible to outside influence. The shift from largely informal elections to the highly structured system of today was a gradual process spanning centuries, heavily influenced by efforts to reduce corruption and political maneuvering.
The Secrecy of the Conclave
The "Seclusion" of the Cardinals
The Conclave is characterized by strict regulations ensuring the isolation and confidentiality of the Cardinals. This seclusion is crucial in preventing external pressures and ensuring a free and impartial election:
- Living Quarters: Cardinals are confined to specific living quarters within the Vatican, often with limited communication with the outside world.
- Daily Routines: Their daily routines are tightly controlled, minimizing opportunities for outside contact.
- Security Measures: The Vatican employs robust security measures to maintain the secrecy of the Conclave, preventing unauthorized access or communication.
The secrecy is designed to create an environment where the Cardinals can freely deliberate and choose the most suitable candidate, unburdened by external influences or pressures.
The Role of the "Secrecy Oath"
All participants in the Conclave take a solemn oath of secrecy, promising to maintain confidentiality regarding the proceedings, even after the Conclave concludes:
- Oath Details: The oath specifically forbids the disclosure of any information relating to the discussions, votes, or any other aspect of the Conclave.
- Penalties for Violation: Violation of the secrecy oath can lead to serious consequences, including excommunication.
- Historical Instances: While breaches of secrecy are rare, historical records indicate that some instances have occurred, albeit with consequences reflecting the gravity of the violation.
The Process of Electing a Pope
The Pre-Conclave Preparations
Several steps precede the Conclave itself:
- Confirmation of Vacancy: The death or resignation of the Pope is officially confirmed, declaring the See vacant.
- Gathering of Cardinals: The College of Cardinals, comprised of Cardinals under 80 years old, gathers in Rome to prepare for the Conclave.
The Voting Procedures
The voting process is rigorous and designed to ensure a fair and legitimate election:
- Ballots: Cardinals cast secret ballots, reflecting their votes for the next Pope.
- Required Majority: A two-thirds majority is required for the election to be valid.
- Inconclusive Rounds: If no candidate receives the necessary majority, multiple voting rounds continue until a Pope is elected.
- Signals: The "fumata bianca" (white smoke) signifies the election of a new Pope, while "fumata nera" (black smoke) indicates that no decision has been reached.
- "Habemus Papam!": This Latin phrase, meaning "We have a Pope!", is announced to the world upon the election of a new Pope.
Post-Election Procedures
Following the election, several key events occur:
- Official Announcement: The new Pope is officially announced to the world.
- Papal Coronation/Installation: A formal ceremony, either a coronation or a simple installation, marks the beginning of the new papacy.
- First Actions: The new Pope undertakes the responsibilities of his office, starting with addressing the faithful and laying out his plans for the future of the Catholic Church.
Conclusion
Papal Conclaves represent a unique blend of history, tradition, and secrecy. Their evolution from chaotic early elections to the highly structured modern process reflects the Church's ongoing efforts to balance tradition with the demands of the modern world. The importance of secrecy, ensured by the physical seclusion of the Cardinals and the solemn Secrecy Oath, guarantees an environment free from outside influences. Understanding the intricate process of electing a new Pope illuminates a critical aspect of the Catholic Church's governance and its continuity throughout history. For a deeper understanding of this fascinating and significant process, further research into the history of specific Papal Conclaves and the lives of influential Cardinals is encouraged. Delve deeper into the intricacies of Papal Conclaves and gain a richer understanding of this pivotal event in Catholic history.

Featured Posts
-
 Rapid Police Response After Fsu Security Breach Did It Quell Student Fears
Apr 22, 2025
Rapid Police Response After Fsu Security Breach Did It Quell Student Fears
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Chainalysis Acquires Alterya Blockchain Meets Ai
Apr 22, 2025
Chainalysis Acquires Alterya Blockchain Meets Ai
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Cassidy Hutchinson Key Witness To January 6th Announces Memoir
Apr 22, 2025
Cassidy Hutchinson Key Witness To January 6th Announces Memoir
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Zuckerberg And Trump A New Era For Tech And Politics
Apr 22, 2025
Zuckerberg And Trump A New Era For Tech And Politics
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Over The Counter Birth Control A New Era Of Reproductive Healthcare After Roe
Apr 22, 2025
Over The Counter Birth Control A New Era Of Reproductive Healthcare After Roe
Apr 22, 2025
