China's Export-Led Growth And The Implications Of Increased Tariffs
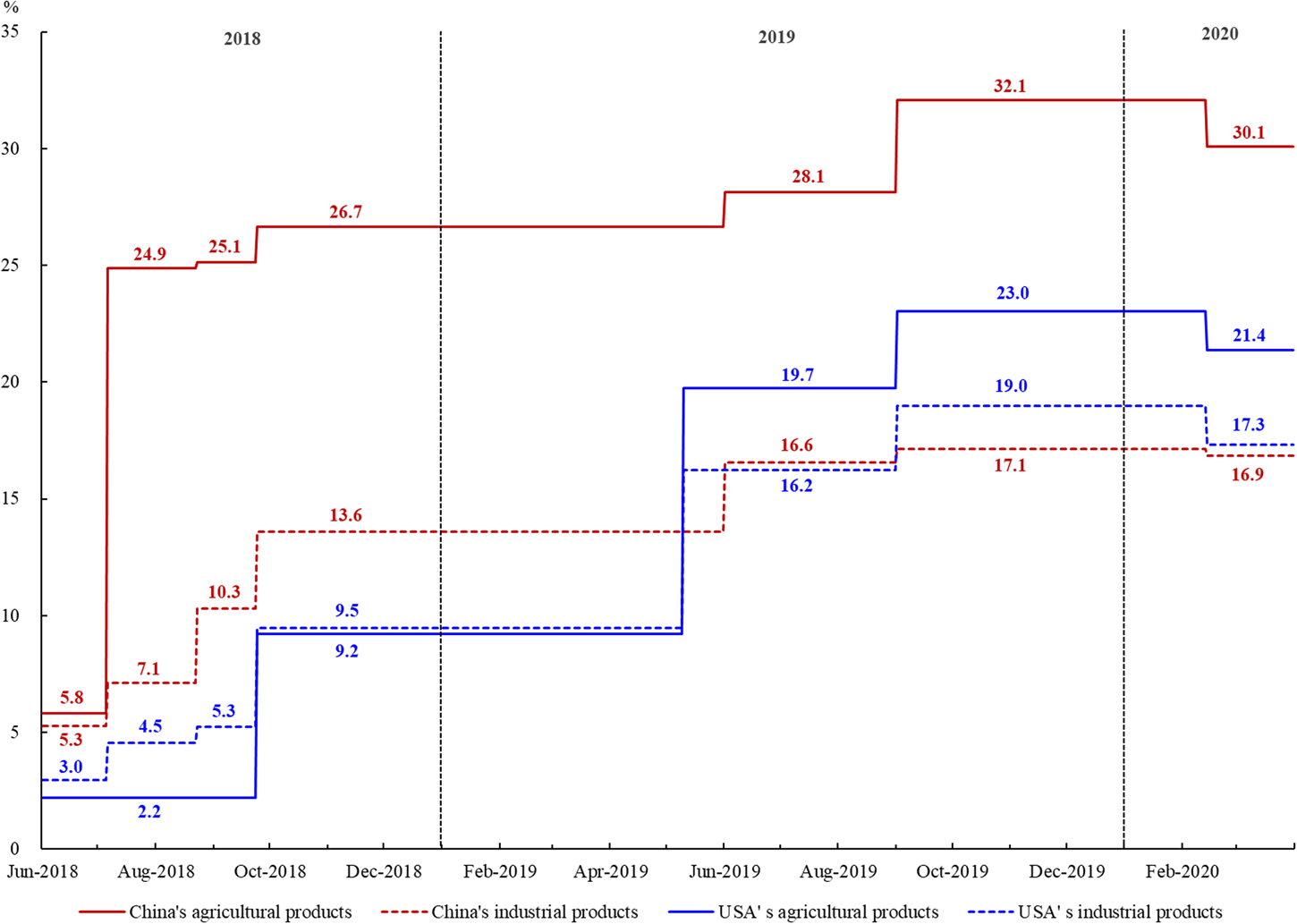
Table of Contents
The Pillars of China's Export-Oriented Economy
China's export success rests on several key pillars. Its vast manufacturing sector, fueled by cheap labor and government subsidies, produces a wide range of goods, from textiles and electronics to machinery and consumer products. The country's integration into global value chains, leveraging its position as a manufacturing hub, has been instrumental in its export dominance. This intricate network allows for efficient production and distribution of goods worldwide.
- Manufacturing hubs and special economic zones: Cities like Shenzhen, Guangzhou, and Shanghai have become global manufacturing powerhouses, attracting substantial foreign direct investment (FDI) and fostering export-oriented industries.
- Export processing zones and their contribution: These zones offer tax incentives and streamlined regulations, further boosting export production and attracting international companies.
- Foreign direct investment (FDI) and its role in exports: FDI has played a critical role, bringing in capital, technology, and management expertise, enhancing China's export capacity and competitiveness.
The Impact of Increased Tariffs on Chinese Exports
Increased tariffs directly impact Chinese export prices and competitiveness. Higher tariffs make Chinese goods more expensive in international markets, reducing their demand and potentially shrinking market share. This can lead to a decline in export volume and revenue, impacting businesses and employment across various sectors. Furthermore, tariffs can lead to trade diversion, with importers shifting sourcing to other countries offering similar goods at lower prices.
- Examples of specific tariffs imposed on Chinese goods: Tariffs on steel, aluminum, and various consumer goods have already significantly impacted Chinese exporters.
- Quantitative analysis of export decline in specific sectors: Empirical data reveals a noticeable decrease in exports of certain goods following tariff imposition, illustrating the tangible effects of trade protectionism.
- Case studies of companies affected by tariff increases: Numerous case studies highlight the challenges faced by Chinese firms, showcasing job losses, factory closures, and strategic shifts in response to tariff pressures.
Impact on Specific Industries
Certain industries are particularly vulnerable to tariff increases. The textile industry, for instance, has experienced significant challenges due to higher import duties in key markets. Similarly, the electronics and steel sectors have felt the pinch, impacting not only these industries directly but also creating ripple effects throughout related supply chains.
- Analysis of job losses and factory closures in affected sectors: Data reveals substantial job losses and factory closures in industries heavily reliant on exports to tariff-imposing countries.
- Discussion of supply chain disruptions due to tariffs: The imposition of tariffs has caused significant disruptions to global supply chains, impacting businesses worldwide.
- Government responses to support affected industries: The Chinese government has implemented various measures to mitigate the negative impacts of tariffs, including financial aid and policy adjustments.
China's Response Strategies to Tariff Increases
Faced with increased tariffs, China has adopted several strategies to mitigate their impact. These include stimulating domestic consumption to reduce reliance on exports, diversifying export markets to reduce dependence on any single market, and focusing on technological advancement to enhance competitiveness.
- Government initiatives to support domestic consumption: Policies aimed at boosting domestic demand, such as infrastructure spending and income support programs, are being implemented.
- Efforts to expand exports to new markets (e.g., Africa, Latin America): China is actively pursuing new export markets in developing economies, seeking to diversify its trading partners and reduce reliance on Western markets.
- Investments in research and development to improve technological competitiveness: China is investing heavily in R&D to upgrade its manufacturing capabilities and enhance its technological edge.
Global Implications of Shifting Trade Dynamics
The escalating trade tensions between China and other major economies have broader global implications. Increased tariffs lead to higher prices for consumers in importing countries, potentially fueling inflation. Furthermore, the disruption of global supply chains impacts businesses worldwide, creating uncertainty and increasing costs. Geopolitical tensions are also exacerbated by these trade disputes.
- Potential for increased inflation in importing countries: Tariffs increase the cost of goods, leading to higher prices for consumers in the importing countries.
- Shifting global supply chain dynamics and their impact on businesses: Businesses are forced to adapt to changing supply chains, impacting costs and efficiency.
- Geopolitical implications of trade tensions between major economies: Trade disputes contribute to broader geopolitical instability and uncertainty.
Understanding the Future of China's Export-Led Growth in a Tariff-Challenged World
Increased tariffs pose significant challenges to China's export-led growth model. However, the Chinese economy has shown remarkable resilience and adaptability in the past. While the short-term impact of tariffs is undeniable, the long-term implications will depend on China's success in implementing its response strategies and adapting to a more complex and potentially less predictable global trade environment. Monitoring these developments is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike. Further research and analysis into the specific sectors impacted by trade policy changes are vital for navigating this evolving landscape. Stay informed about the evolving landscape of China's export-led growth and the ongoing implications of increased tariffs. Understanding these dynamics is essential for businesses and policymakers navigating the complexities of global trade.

Featured Posts
-
 Car Dealers Renew Opposition To Ev Mandates Industry Fights Back
Apr 22, 2025
Car Dealers Renew Opposition To Ev Mandates Industry Fights Back
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Higher Stock Prices Higher Risks What Investors Should Know
Apr 22, 2025
Higher Stock Prices Higher Risks What Investors Should Know
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Anchor Brewing Company Shuttering Impact On The Craft Beer Industry
Apr 22, 2025
Anchor Brewing Company Shuttering Impact On The Craft Beer Industry
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Secret Service Investigation Concludes Cocaine Found At White House
Apr 22, 2025
Secret Service Investigation Concludes Cocaine Found At White House
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Closer Security Partnership Between China And Indonesia
Apr 22, 2025
Closer Security Partnership Between China And Indonesia
Apr 22, 2025
