China's Rare Earth Export Curbs Hamper Tesla's Optimus Robot Development

Table of Contents
China's Dominance in Rare Earth Mining and Processing
China holds an unparalleled position in the global rare earth market, controlling a staggering majority of mining and refining operations. These minerals are not just economically important; they are strategically vital for numerous high-tech industries, including robotics, clean energy technologies, and advanced military applications. This dominance gives China significant leverage in the global supply chain.
- Market Share: China accounts for over 70% of global rare earth production, a figure that underscores its unparalleled influence.
- Key Elements for Optimus: Neodymium and dysprosium, two critical rare earth elements, are essential for the powerful and efficient motors that power Optimus's movements and functionalities. These magnets are crucial for achieving the robot's desired performance levels.
- Geographic Concentration: The majority of the world's rare earth mines are concentrated within China, further solidifying its control over this vital resource.
The Role of Rare Earths in Optimus Robot Production
Rare earth elements are not merely supplementary components in Optimus; they are integral to its very functionality. Their unique magnetic properties are indispensable for several key robot components.
- Rare Earth Magnets: High-strength neodymium magnets are extensively used in Optimus's motors, enabling the precision and power necessary for complex movements and tasks. These magnets are far more powerful than alternatives, making them crucial for the robot's performance.
- Cost Impact: Scarcity of rare earths directly translates to increased production costs for Tesla. Securing these materials from alternative sources will inevitably be more expensive, impacting the robot's final price.
- Manufacturing Delays: Any disruption in the supply chain, stemming from export restrictions or geopolitical instability, can lead to significant delays in Optimus robot manufacturing and its subsequent market launch.
Impact of Export Restrictions on Tesla's Supply Chain
China's export restrictions on rare earth elements pose a considerable challenge to Tesla's ability to source the materials necessary for Optimus production. This reliance on a single major supplier creates significant vulnerabilities.
- Increased Costs: Sourcing rare earths from alternative suppliers, often located in politically unstable regions or with less efficient extraction processes, results in substantially higher costs.
- Geopolitical Risks: Over-reliance on a single nation for such critical materials carries considerable geopolitical risk. Changes in international relations or unexpected policy shifts could severely disrupt Tesla's supply chain.
- Market Entry Delays: Supply chain disruptions directly translate to potential delays in the Optimus robot's rollout and market entry, potentially impacting Tesla's competitive position in the burgeoning robotics market.
Tesla's Strategies to Mitigate Rare Earth Dependency
Tesla is likely pursuing several strategies to mitigate its dependence on Chinese rare earth supplies. This includes exploring alternative materials and technologies, as well as investing in diversification efforts.
- Recycling Technologies: Investment in advanced rare earth recycling technologies can help reduce the reliance on newly mined materials, increasing resource efficiency and sustainability.
- Alternative Magnet Technologies: Research into and development of alternative magnet technologies that require fewer or no rare earth elements is a crucial long-term strategy.
- Supply Chain Diversification: Tesla is likely actively seeking partnerships and agreements with companies in other regions to secure more diverse and reliable rare earth supplies.
The Broader Implications for the Robotics Industry
China's rare earth export policies have wide-ranging implications for the entire global robotics industry. The current system emphasizes the need for more resilient and diversified supply chains.
- Increased Production Costs: The increased cost of rare earths will inevitably lead to higher production costs across the board for robotics manufacturers, impacting the affordability and accessibility of robots.
- Geopolitical Tensions: Geopolitical instability and trade disputes related to rare earths create further uncertainty and risk for the industry.
- Accelerated Research: The scarcity of rare earths is driving accelerated research into alternative materials and technologies within the robotics industry, pushing innovation and encouraging a transition to more sustainable practices.
Conclusion: Navigating the Rare Earth Challenge for Optimus Robot Development
China's influence on the global rare earth market presents a significant challenge to Tesla's Optimus robot development and the broader robotics industry. The reliance on a single major supplier introduces significant vulnerabilities in terms of cost, geopolitical stability, and supply chain resilience. Tesla, and the robotics industry as a whole, face the critical need to diversify sourcing, invest in recycling, and research alternative materials. The future of robotics, and specifically the success of projects like Tesla's Optimus robot, hinges on addressing the challenges presented by China's rare earth export curbs. Further research and innovative solutions are crucial for securing a resilient and sustainable supply chain for the future of this crucial technology.

Featured Posts
-
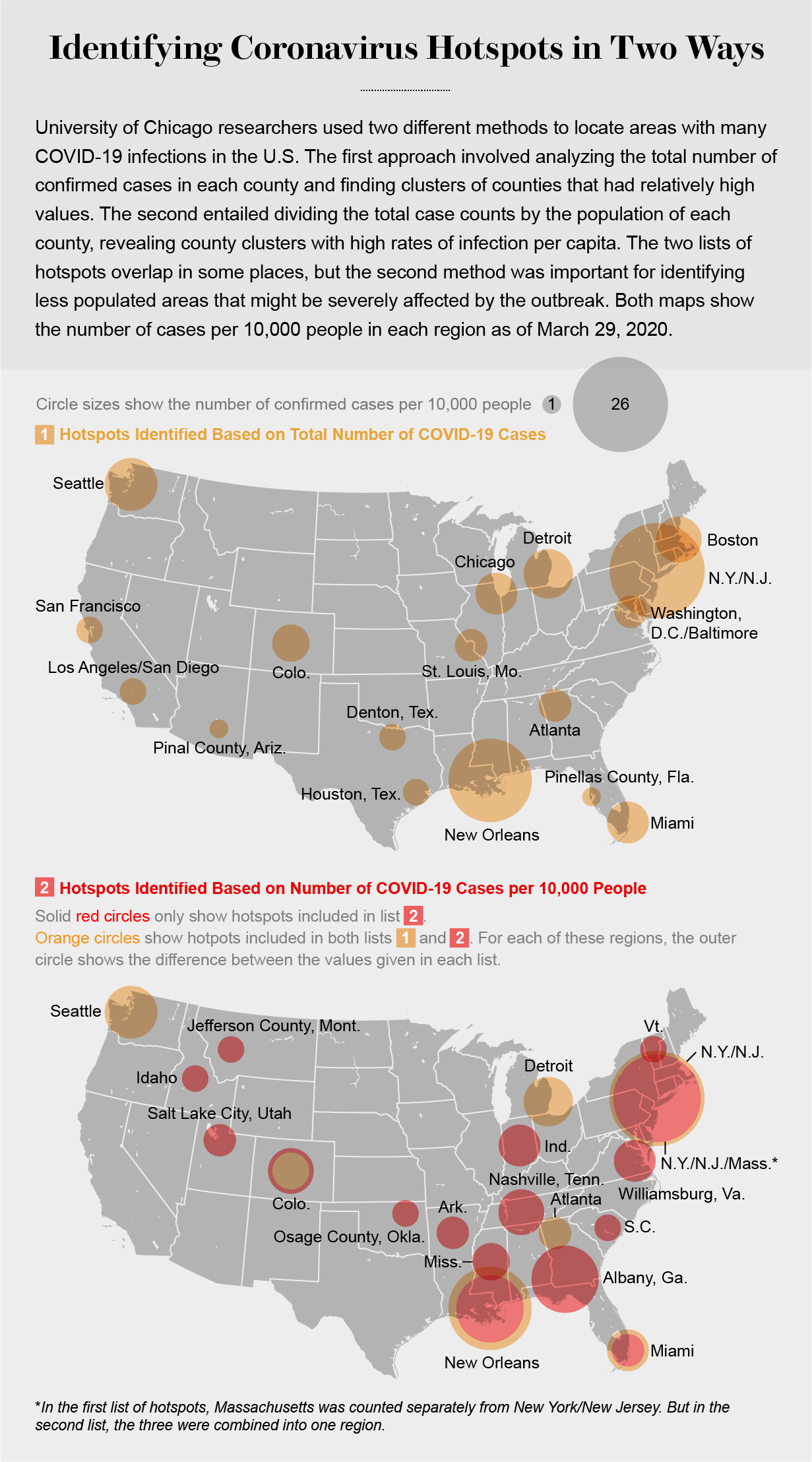 Mapping The Rise Of New Business Hot Spots Across The Nation
Apr 24, 2025
Mapping The Rise Of New Business Hot Spots Across The Nation
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Hollywood Shutdown The Impact Of The Writers And Actors Strike
Apr 24, 2025
Hollywood Shutdown The Impact Of The Writers And Actors Strike
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Harvards Lawsuit Against Trump Administration Progress Towards A Resolution
Apr 24, 2025
Harvards Lawsuit Against Trump Administration Progress Towards A Resolution
Apr 24, 2025 -
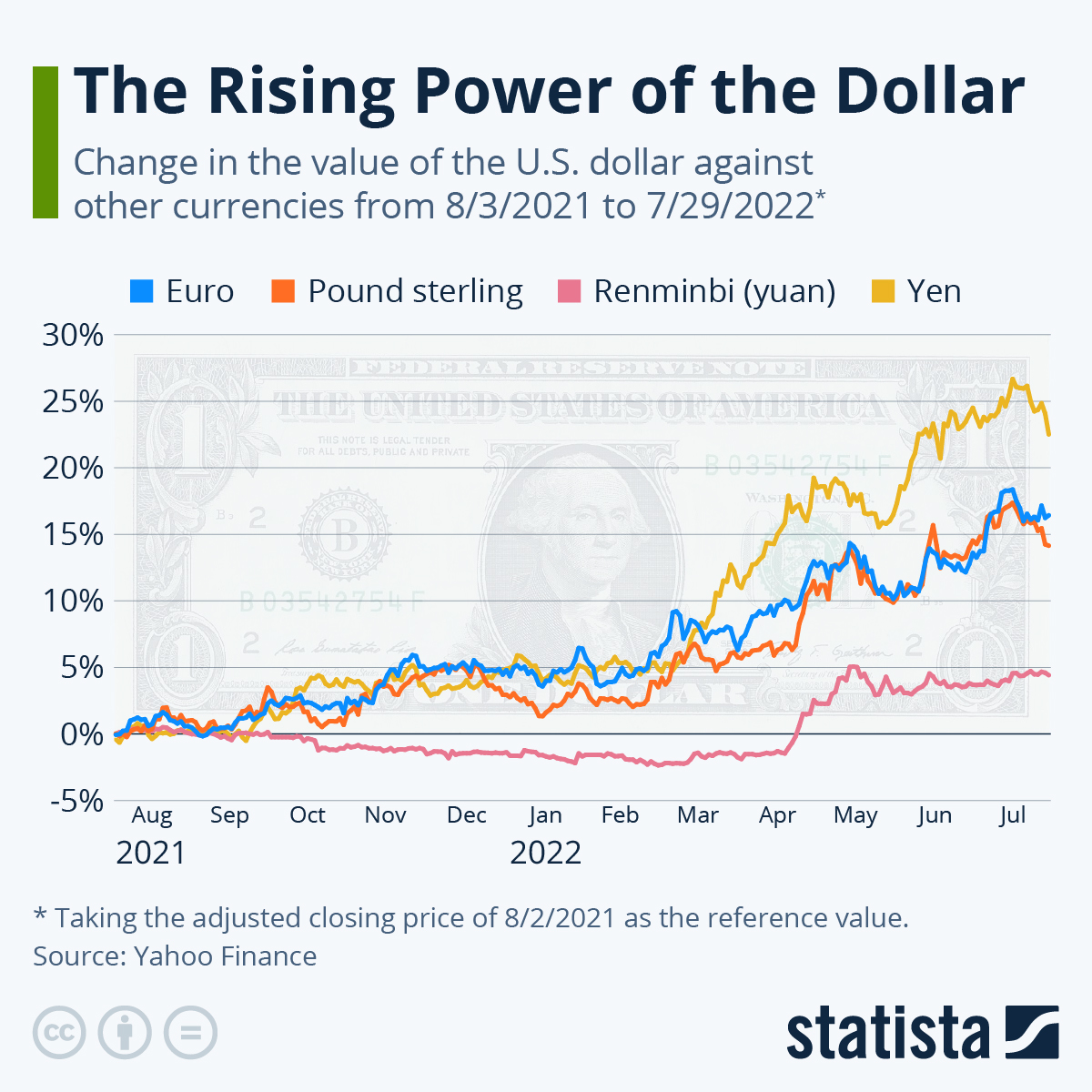 Usd Gains Momentum Trumps Change In Tone Impacts Dollars Performance Against Major Currencies
Apr 24, 2025
Usd Gains Momentum Trumps Change In Tone Impacts Dollars Performance Against Major Currencies
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Whataburger Video Propels Hisd Mariachi To Uil State Competition
Apr 24, 2025
Whataburger Video Propels Hisd Mariachi To Uil State Competition
Apr 24, 2025
