Understanding Stock Market Valuations: A BofA-Informed View
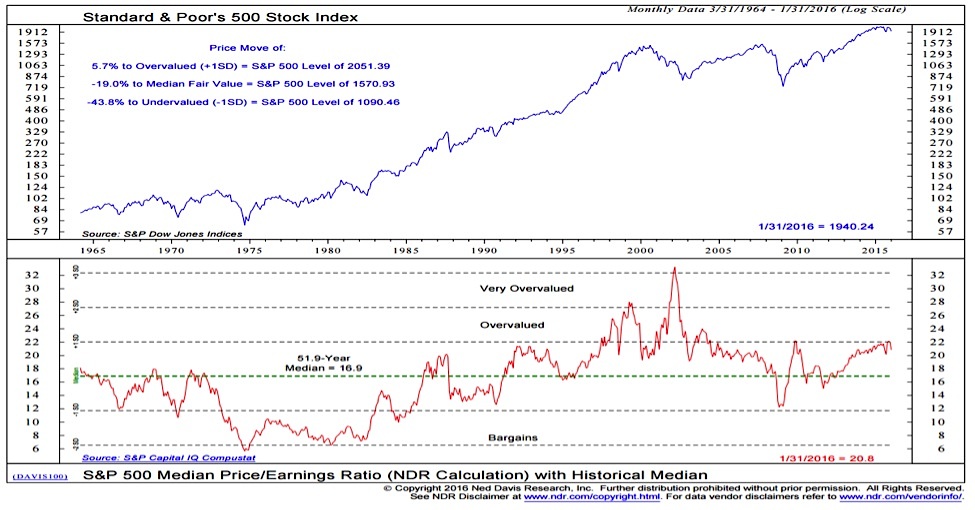
Table of Contents
Key Valuation Metrics Explained
Stock market valuation is the process of determining the economic worth of a company's stock. It's crucial because it helps investors determine whether a stock is fairly priced, undervalued, or overvalued relative to its intrinsic value and future potential. Accurate valuation is fundamental to successful long-term investing. Let's delve into some key metrics:
Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E):
The Price-to-Earnings ratio (P/E) is one of the most widely used valuation metrics. It represents the price an investor pays for each dollar of a company's earnings. A high P/E ratio might suggest investors expect high future growth, but it could also indicate overvaluation. Conversely, a low P/E ratio might signal undervaluation or potential problems with the company's earnings. However, it's crucial to remember that the P/E ratio is just one piece of the puzzle.
- Formula for calculating P/E ratio: Market Price per Share / Earnings per Share (EPS)
- Importance of comparing P/E ratios within the same industry: Comparing P/E ratios across different sectors can be misleading due to varying industry dynamics and growth prospects. A P/E ratio of 20 might be high for one industry but low for another.
- Potential impact of earnings manipulation on P/E ratios: Companies might manipulate earnings to artificially inflate or deflate their P/E ratios, making it essential to scrutinize a company's financial statements thoroughly.
For example, let's imagine Company A has a market price of $100 and EPS of $5, resulting in a P/E ratio of 20. Company B, in the same sector, has a market price of $80 and EPS of $4, resulting in a P/E ratio of 20. While their P/E ratios are identical, a deeper dive into their financials might reveal differences that justify the valuation discrepancies.
Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B):
The Price-to-Book ratio (P/B) compares a company's market capitalization to its book value of equity. Book value represents the net asset value of a company, calculated as total assets minus total liabilities. P/B is often used in value investing to identify potentially undervalued companies.
- Formula for calculating P/B ratio: Market Price per Share / Book Value per Share
- How P/B ratios are used to identify undervalued companies: A low P/B ratio might indicate that the market undervalues a company's assets.
- The impact of intangible assets on P/B ratios: Companies with significant intangible assets (like brands or intellectual property) might have higher P/B ratios than companies with primarily tangible assets. This is because intangible assets aren't fully reflected in the book value.
The difference between book value and market value is crucial. Book value is an accounting measure, while market value reflects investor sentiment and expectations for future growth.
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis:
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) analysis is a more complex, intrinsic valuation method. It estimates a company's value by discounting its projected future cash flows back to their present value. This approach attempts to determine a company’s intrinsic value.
- Steps involved in performing a DCF analysis: Projecting future free cash flows, selecting an appropriate discount rate (reflecting the risk), and calculating the present value of those cash flows.
- The role of discount rate in DCF analysis: The discount rate is crucial because it reflects the risk associated with the investment. A higher discount rate results in a lower present value.
- Sensitivity analysis in DCF valuation: Performing sensitivity analysis, examining how changes in key assumptions impact the valuation, is critical.
DCF analysis requires significant forecasting and assumptions about future growth and profitability, making it a more subjective method than P/E or P/B ratios.
BofA's Approach to Stock Market Valuation
Bank of America's analysts likely utilize a combination of these metrics and other factors for stock market valuation. They probably incorporate macroeconomic analysis, considering factors like interest rates, inflation, and economic growth. While specific internal methodologies aren’t usually public, their research reports might offer insights into their valuation approach.
- Potential use of qualitative factors by BofA analysts: BofA analysts likely consider qualitative factors such as management quality, competitive landscape, and industry trends.
- BofA's potential emphasis on long-term growth prospects: BofA's valuation likely incorporates assessments of a company's long-term growth potential.
- How BofA might incorporate risk assessment into valuations: Risk assessment, considering factors such as debt levels and industry cyclicality, is integral to their valuation process.
Accessing BofA's research reports (if publicly available) can provide valuable insights into their valuation process and specific stock recommendations.
Interpreting Valuation Data & Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Interpreting valuation ratios requires context. Relying solely on a single metric is dangerous. Understanding a company's fundamentals, industry dynamics, and competitive landscape is crucial.
- The danger of comparing companies across different sectors using the same metrics: Direct comparison of valuation ratios across different sectors can be misleading due to differences in industry growth rates, risk profiles, and accounting practices.
- The effect of market sentiment on stock prices: Short-term market sentiment can significantly impact stock prices, creating discrepancies between market value and intrinsic value.
- The need for thorough due diligence before investing: Thorough due diligence, including analyzing financial statements, competitive landscape, and management quality, is essential before making any investment decisions.
Conclusion
Understanding stock market valuations is crucial for successful investing. By mastering key metrics like P/E, P/B, and DCF analysis, and by considering a BofA-informed perspective which incorporates macroeconomic factors and qualitative analysis, you can make more informed investment decisions. While no valuation method is foolproof, a multi-faceted approach combining quantitative and qualitative analysis offers the best chance of identifying both undervalued and overvalued stocks. Start improving your stock market valuation skills today by researching BofA's market analysis and practicing these methods. Learn to effectively utilize stock valuation techniques and master the art of equity valuation.

Featured Posts
-
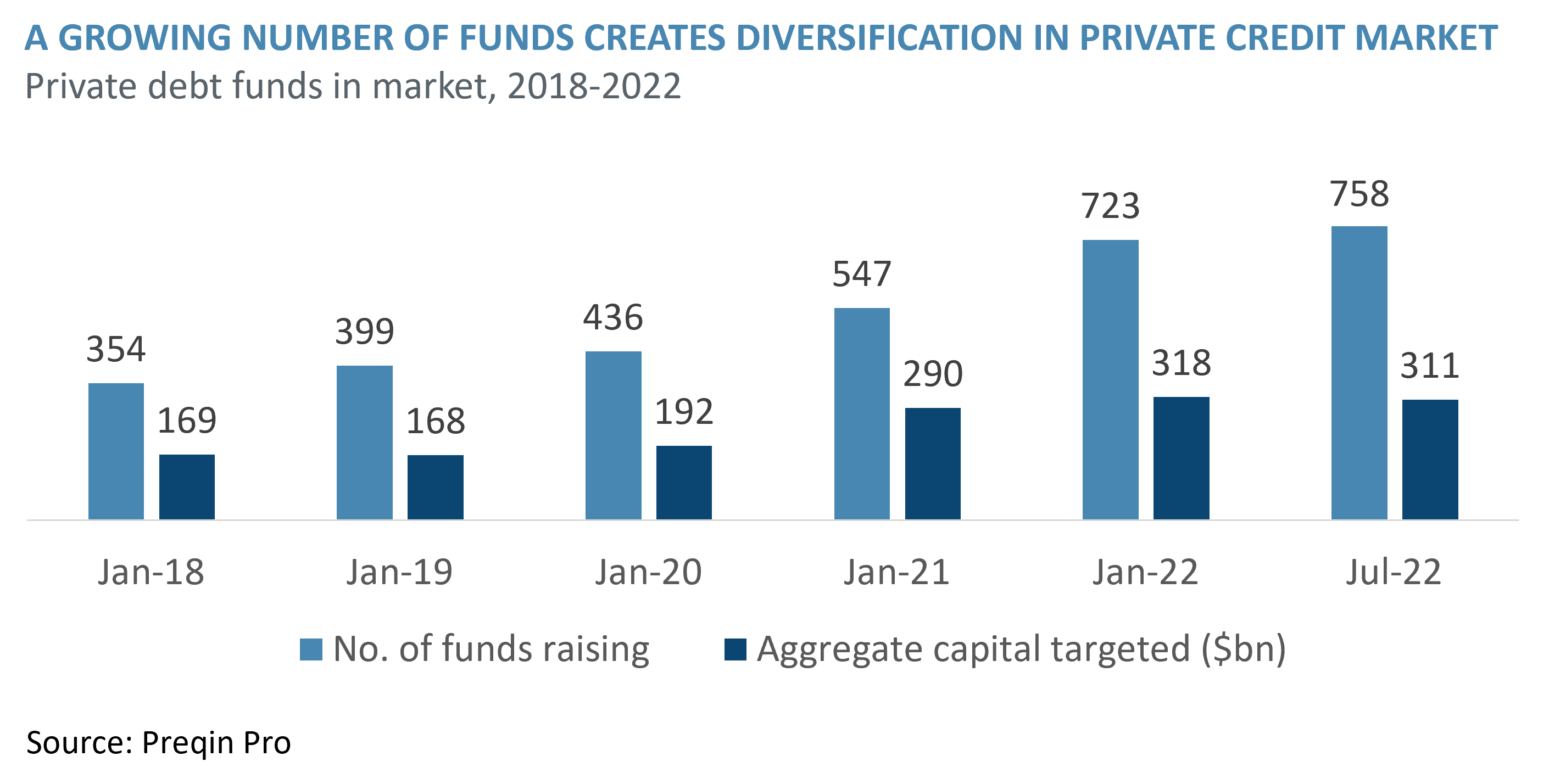 5 Essential Dos And Don Ts Succeeding In The Private Credit Market
Apr 26, 2025
5 Essential Dos And Don Ts Succeeding In The Private Credit Market
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Pete Hegseth Faces Pentagon Backlash Exclusive Details On Polygraph Tests And Leaks
Apr 26, 2025
Pete Hegseth Faces Pentagon Backlash Exclusive Details On Polygraph Tests And Leaks
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Ceos Sound Alarm Trump Tariffs Crippling Economy Consumers Fearful
Apr 26, 2025
Ceos Sound Alarm Trump Tariffs Crippling Economy Consumers Fearful
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Ray Epps Sues Fox News For Defamation Over Jan 6 Coverage Key Details
Apr 26, 2025
Ray Epps Sues Fox News For Defamation Over Jan 6 Coverage Key Details
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Nintendos Action Ryujinx Switch Emulator Development Ends
Apr 26, 2025
Nintendos Action Ryujinx Switch Emulator Development Ends
Apr 26, 2025
