Why Nike Sneaker Production Remains A Challenge For Robots
Table of Contents
The Dexterity and Precision Hurdle
H3: Fine Motor Skills Required for Sneaker Assembly:
Sneaker assembly is a surprisingly intricate process requiring a high degree of dexterity and precision. Tasks such as gluing the sole to the upper, precisely stitching various components, and carefully attaching laces demand fine motor skills that current robotic systems struggle to replicate. Robots currently lack the nuanced touch and adaptability necessary for consistently flawless execution of these steps.
- Precise gluing: Applying the correct amount of adhesive to ensure a strong bond without excess spillage.
- Intricate stitching: Following complex patterns with consistent tension and stitch length.
- Delicate lace insertion: Threading laces through eyelets without damaging the material.
These tasks require a level of robotic dexterity and precision assembly far beyond the capabilities of current industrial robots, highlighting the limitations of sneaker manufacturing automation in its current state.
H3: Adaptability to Variations in Materials and Designs:
Nike's success stems partly from its diverse range of materials and designs. From supple leather and breathable mesh to innovative synthetic materials, the variety poses a significant hurdle for robotic systems. Robots are typically programmed for specific tasks and materials. Adapting them to handle the variability inherent in Nike's product line requires significant reprogramming and adjustments, making them inefficient for diverse production runs.
- Material variability: Leather, mesh, synthetics, and various blends all have different properties affecting assembly techniques.
- Design flexibility: Constant design innovation means robots must adapt quickly to new models and configurations.
The need for material adaptability and design flexibility underscores the requirement for more advanced, AI-powered robotics capable of learning and adapting to changing conditions.
The Cost and Economic Viability Factor
H3: High Initial Investment and Maintenance Costs:
Implementing robotic systems in sneaker factories demands substantial upfront investment. The cost includes purchasing sophisticated robotic arms, specialized programming software, and the necessary infrastructure. Furthermore, ongoing maintenance and repair, often requiring highly skilled technicians, contribute significantly to the overall expense.
- Specialized programming: Programming robots to perform complex assembly tasks necessitates skilled programmers and extensive testing.
- Skilled technicians: Maintaining and repairing advanced robotic equipment requires specialized expertise.
The high robotics cost, coupled with the need for continuous maintenance, directly impacts the automation ROI and makes sneaker manufacturing economics a critical factor in evaluating the viability of full-scale automation.
H3: Return on Investment (ROI) Considerations:
The economic feasibility of robotic automation in sneaker production depends on a careful cost-benefit analysis. While robots offer potential labor savings, the high initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs need to be weighed against the potential gains. For smaller-scale production runs, achieving a sufficient manufacturing automation ROI is currently challenging.
- Production volume: Higher production volumes can help spread the initial investment cost and improve ROI.
- Labor costs: Labor costs in different regions significantly impact the attractiveness of automation.
- Robot efficiency: The actual efficiency of the robotic system in terms of speed and error rate directly affects ROI.
This necessitates a thorough examination of Nike production efficiency potential in relation to its overall cost structure.
The Need for Human-Robot Collaboration
H3: Collaborative Robots (Cobots) as a Potential Solution:
Collaborative robots, or cobots, offer a promising pathway toward increased automation. Cobots are designed to work alongside human workers, handling specific tasks where robots excel (e.g., repetitive gluing) while humans focus on intricate or unpredictable steps. This approach leverages the strengths of both human dexterity and robotic precision.
- Increased flexibility: Cobots adapt more easily to variations in materials and designs compared to fully automated systems.
- Cost-effectiveness: The initial investment and maintenance costs for cobots are generally lower than for fully automated systems.
- Safety features: Cobots are equipped with safety mechanisms to prevent accidents when working alongside humans.
This human-robot collaboration model maximizes efficiency and minimizes the risks associated with complete automation.
H3: The Future of Human-Robot Teams in Sneaker Production:
The future of Nike sneaker production likely involves increasingly sophisticated human-robot teams. Advancements in AI in manufacturing, coupled with improved robotic dexterity and more robust sensor technologies, will pave the way for more agile and adaptable robotic systems.
- Advanced AI: AI-powered robots will be able to learn and adapt to new tasks and materials more efficiently.
- Improved dexterity: Future robots may have more sophisticated grippers and manipulators enabling more precise and versatile movements.
- More robust sensors: Improved sensors will allow robots to better perceive their environment and react to unforeseen circumstances.
These developments are crucial for achieving a higher degree of automation while maintaining the flexibility and quality demanded by Nike's diverse product line.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Challenges of Nike Sneaker Production Automation
While fully automating Nike sneaker production remains a significant challenge, the hurdles are not insurmountable. The complexities revolve around the need for superior robotic dexterity, the high cost of implementation, and the inherent value of human-robot collaboration. However, ongoing advancements in AI and robotics are gradually addressing these limitations. Continued research and development in areas such as advanced automation, improving Nike sneaker production automation advancements, and exploring the future of Nike sneaker manufacturing robotics are crucial for improving efficiency and meeting the ever-growing demand for Nike sneakers. Let's continue to explore innovative ways to improve Nike's production efficiency through robotics.

Featured Posts
-
 Palisades Fire A Comprehensive List Of Celebrities Who Lost Homes
Apr 22, 2025
Palisades Fire A Comprehensive List Of Celebrities Who Lost Homes
Apr 22, 2025 -
 The Importance Of Middle Management Bridging The Gap Between Leadership And Employees
Apr 22, 2025
The Importance Of Middle Management Bridging The Gap Between Leadership And Employees
Apr 22, 2025 -
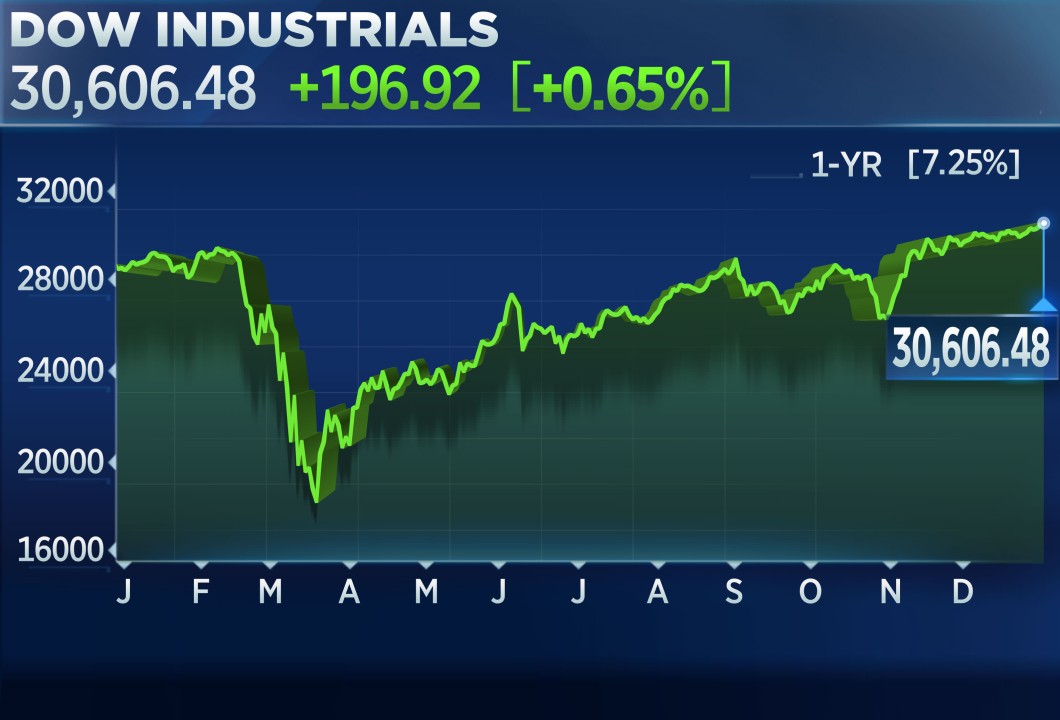 Trade War Impact Todays Stock Market Analysis And Dow Futures
Apr 22, 2025
Trade War Impact Todays Stock Market Analysis And Dow Futures
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Open Ai Facing Ftc Investigation A Deep Dive Into The Issues
Apr 22, 2025
Open Ai Facing Ftc Investigation A Deep Dive Into The Issues
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Russias Easter Truce Ends Renewed Fighting In Ukraine
Apr 22, 2025
Russias Easter Truce Ends Renewed Fighting In Ukraine
Apr 22, 2025
