Decoding The Canadian Dollar's Contrasting Movements In The Global Currency Market
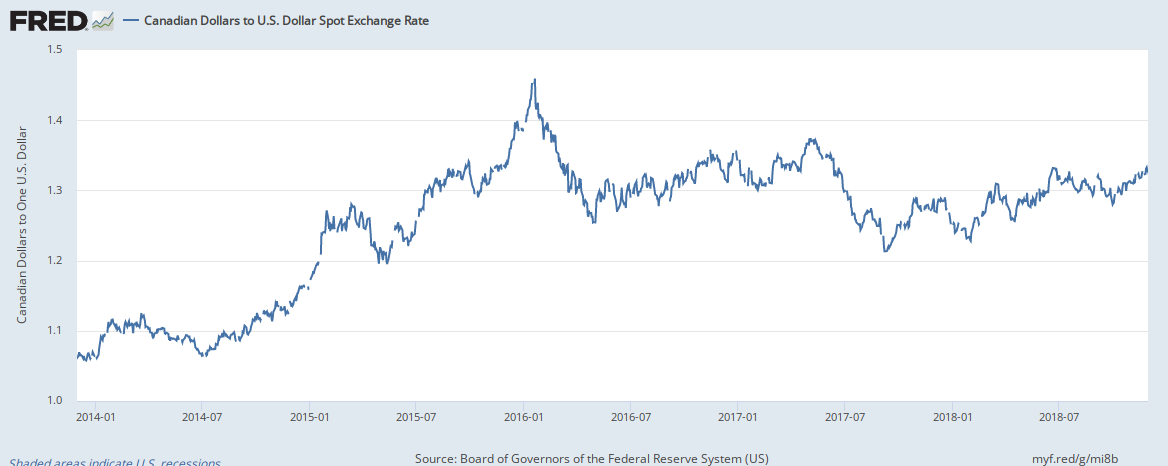
Table of Contents
Impact of Commodity Prices on the Canadian Dollar
The Canadian economy is heavily reliant on natural resource exports, making commodity prices a significant driver of the Canadian dollar's value. Understanding this relationship is key to predicting CAD movements.
The Role of Oil and Gas
Canada's economy is significantly tied to oil and gas production. Fluctuations in global energy markets directly impact the CAD's value.
- Increased oil prices generally strengthen the CAD. Higher global demand for oil leads to increased demand for the Canadian dollar, as it's used to purchase Canadian oil and gas. This increased demand pushes the CAD's value upward.
- Decreased oil prices typically weaken the CAD. Conversely, when oil prices fall, the demand for the CAD decreases, leading to a depreciation of the currency.
- Geopolitical events affecting oil supply significantly influence the CAD. Events like conflicts in oil-producing regions or sanctions on major exporters can cause sharp price swings and consequently affect the CAD.
Detailed explanation: The mechanism is straightforward: higher demand for oil increases demand for the CAD, leading to appreciation. This is because buyers need Canadian dollars to purchase Canadian oil. Conversely, lower demand weakens the CAD. For example, the sharp drop in oil prices in 2014 significantly weakened the Canadian dollar. Recent fluctuations in global energy markets due to geopolitical tensions have shown this relationship in action.
Other Commodity Influences
Beyond oil and gas, other commodities play a role in the CAD's value. Canada is a major exporter of several resources.
- Strong demand for Canadian lumber boosts the CAD. The global construction industry's reliance on Canadian lumber means high demand translates into stronger CAD performance.
- Global economic slowdown impacting metal demand can weaken the CAD. Reduced global industrial activity decreases demand for Canadian metals like nickel, aluminum, and zinc, weakening the Canadian dollar.
- Seasonal variations in agricultural exports can have minor but noticeable impacts. While less impactful than oil or metals, seasonal changes in agricultural exports can create short-term fluctuations in the CAD.
Detailed explanation: While oil and gas dominate, diversification across commodities lessens the CAD's dependence on any single sector. A downturn in one sector's commodity price can be partially offset by strength in another, leading to a more stable, though not necessarily strong, currency.
Influence of Interest Rate Differentials
Interest rates play a crucial role in determining the attractiveness of a currency to foreign investors. The Bank of Canada's monetary policy directly impacts the CAD.
Bank of Canada Monetary Policy
The Bank of Canada's decisions regarding interest rates significantly influence the CAD's value.
- Increased interest rates make CAD-denominated assets more attractive to foreign investors. Higher interest rates offer better returns, drawing foreign investment and strengthening the CAD.
- Interest rate hikes often signal economic strength, further boosting the CAD. Raising interest rates is often a response to a growing economy, reinforcing the positive sentiment around the Canadian dollar.
- Conversely, interest rate cuts weaken the CAD. Lowering interest rates can make CAD-denominated assets less attractive, leading to capital outflow and a weaker currency.
Detailed explanation: The concept of "carry trade" comes into play here. Investors borrow in low-interest rate currencies and invest in high-interest rate currencies to profit from the difference. Higher Canadian interest rates attract these trades, increasing demand for the CAD. Inflation and economic growth forecasts heavily influence the Bank of Canada's interest rate decisions.
Comparison with Other Major Currencies
The CAD's value isn't determined in isolation; it's influenced by its relative value compared to other major currencies.
- Higher interest rates in Canada compared to the US may strengthen the CAD. If Canadian interest rates exceed those in the US, investors may shift funds to Canada, increasing demand for the CAD.
- Conversely, lower interest rates in Canada may weaken the CAD relative to other currencies. Lower rates make the CAD less attractive compared to currencies with higher yields.
- These comparisons are dynamic and constantly evolving. Global economic conditions constantly shift the relative attractiveness of different currencies.
Detailed explanation: Global economic conditions play a major role. A stronger US economy, for instance, could strengthen the US dollar relative to the CAD, even if Canadian interest rates are higher.
Geopolitical Factors and Global Economic Conditions
Beyond domestic factors, global events significantly impact the Canadian dollar.
Global Economic Growth
Global economic health directly affects the Canadian economy and, consequently, the CAD.
- Global recessionary periods often weaken the CAD. Reduced global demand for Canadian exports leads to a weaker currency.
- Economic growth in key trading partners (e.g., US) has a particularly strong effect. The US is Canada's largest trading partner, making US economic performance critical for the CAD.
Detailed explanation: The interconnectedness of the global economy cannot be overstated. A slowdown in major economies significantly impacts Canadian exports and investment, putting downward pressure on the CAD.
Geopolitical Risks
Uncertainty created by geopolitical events can lead to volatility in the CAD.
- Trade disputes with major trading partners can negatively affect the CAD. Trade wars or disputes disrupt trade flows, impacting the Canadian economy and currency.
- Political uncertainty can lead to capital flight and weaken the CAD. Political instability creates uncertainty, pushing investors to move their funds elsewhere, weakening the CAD.
Detailed explanation: Events like Brexit, the US-China trade war, and various international conflicts have historically impacted the CAD, demonstrating the currency's sensitivity to global geopolitical risks.
Conclusion
The Canadian dollar's movements are complex, driven by a combination of commodity prices, interest rate differentials, and global economic and geopolitical conditions. Understanding these interconnected factors is crucial for navigating the complexities of international trade and investment involving the Canadian dollar. By carefully monitoring these key indicators—commodity prices, Bank of Canada interest rate announcements, global economic growth forecasts, and geopolitical events—individuals and businesses can better predict and manage the risks associated with fluctuations in the Canadian dollar exchange rate. To stay informed about the latest developments affecting the Canadian dollar and refine your trading strategies, continue researching economic indicators and global market trends. Stay ahead of the curve by continually monitoring the factors that impact the Canadian dollar exchange rate and its various influences.

Featured Posts
-
 Teslas Q1 Earnings Political Controversy Impacts Financial Results
Apr 24, 2025
Teslas Q1 Earnings Political Controversy Impacts Financial Results
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Trump Supporter Ray Epps Defamation Suit Against Fox News Jan 6th Falsehoods Allegations
Apr 24, 2025
Trump Supporter Ray Epps Defamation Suit Against Fox News Jan 6th Falsehoods Allegations
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Open Ais 2024 Event Easier Voice Assistant Creation
Apr 24, 2025
Open Ais 2024 Event Easier Voice Assistant Creation
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Btc Price Increase A Look At The Role Of Trumps Policies And Fed Decisions
Apr 24, 2025
Btc Price Increase A Look At The Role Of Trumps Policies And Fed Decisions
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Sharks And A Tragedy A Swimmers Disappearance And Body Found On Israeli Coast
Apr 24, 2025
Sharks And A Tragedy A Swimmers Disappearance And Body Found On Israeli Coast
Apr 24, 2025
